

Designing and implementing Workplace Health and Safety Systems (WHS) management systems requires an understanding of where the organisation IS and where it wants to GO.
Systems management systems provide a baseline for improvement.
What are Workplace Health and Safety Management systems?
WHS&E systems are comprehensive and integrated systems designed to ensure all work in an organisation is conducted safely.
It should be fully documented, accessible and comprehensible to all stakeholders
Why have management systems?
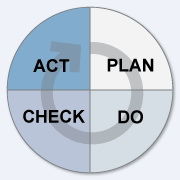 Successful Management Systems are based on the tried and true Plan – Do – Check – Act (PDCA) cycle.
Successful Management Systems are based on the tried and true Plan – Do – Check – Act (PDCA) cycle.
PLAN – Establish objectives and make plans (analyse your organization's situation, establish your overall objectives and set your interim targets, and develop plans to achieve them). DO - Implement your plans (do what you planned to). CHECK – Measure your results (measure/monitor how far your actual achievements meet your planned objectives). ACT– Correct and improve your plans and how you put them into practice (correct and learn from your mistakes to improve your plans in order to achieve better results next time).
Systems designed, implemented and managed correctly ensure everything is in place and the organisations WHSE performance will continuously improve.
No System VS Basic System
| ACTIVITY | NO SYSTEM | BASIC SYSTEM |
| Planning of WHSE Activity | Not planned | Encourages forward planning |
| Definition of Responsibilities | Not defined | Defined for everyone |
| Hazard Identification | Undefined and controlled | Most identified and controlled proactively |
| Risk Control Responsibility | Dependent on individuals | Described in procedures |
| Risk Control Monitoring and review | Review occurs after an incident | Review occurs regularly |
| Systematic risk control | Immediate problem fixed and forgotten | Controls applied to problems in other areas |
| Public & Supplier Risks | Focus on own site | Public and supplier risks planned and managed |
To design a management system we need to consider:
What level of effectiveness of existing workplace consultative and communication arrangements are in place?
Where are you now – where do you want to be?
Consult with stakeholders through formal or informal mechanisms
Who should be consulted?
A number of parties will have critical information and knowledge about an organisations needs and priorities. For example:
Senior management, frontline managers, Supervisors
Design the System to Match Your Needs
WHSE management systems may be:
Off-the-shelf models or developed in house
What makes an effective WHSE management system?
Management commitment drives improvement through consultation
Everyone is involved in making it work
Safety becomes part of everyday business
The focus is on preventing injuries
The system is not too complicated
The system is reviewed regularly
Training and information is provided for all people
Audits
A health and safety audit is a comprehensive check of all objects and processes within the workplace that may present a risk or hazard.
In other words audits are used to check you are doing what you said you would do.
Audits must be carried out on a regular basis to establish what work has to be done to keep premises without risk or hazard to workers and non-workers.
Audits are a great opportunity to get involved in identifying and reporting hazards and assessing risk.
You could be asked to answer questions about your work for an audit, or an auditor might observe you at work to detect any safety and health problems.
Non Conformances
Non-Conformances are non-compliances found during a WHSE audit. The following non-conformities may be issued by an auditor during an audit.
A Finding which may move towards a non-conformity, usually supported by a recommendations
Observations - Failure to meet a requirement of the standard. Organisations needs to demonstrate they are able to comply with the clause within a specific timescale.
Performance Indicators
Performance indicators or KPIs (key Performance Indicators) assist organisations to monitor health and safety performance and evaluate improvement strategies.
A suitable mix of performance indicators that incorporates both positive and negative indicators is needed to provide a comprehensive view of WHS performance.
Negative Indicator examples:
Positive Indicator examples:
Evidence of WHSE in purchasing goods, services and personnel
Tools and Techniques
Common Problems with Management Systems